Overview of Systematic Sampling
SYSTEMATIC
SAMPLING
By: UJJAINI DALAL
CHRIST UNIVERSITY, BANGALORE
Systematic sampling is a commonly employed technique if the complete and up-to-date list of the sampling units in available. This consists in selecting only the first unit at random, the rest being automatically selected according to some predetermined pattern involving regular spacing of units. Systematic sampling is a statistical method that researchers use to zero down on the desired population they want to research. Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of probability sampling in which each member of the group is selected at regular periods to form a sample.
How Systematic Sampling Works
When we are sampling, ensure you represent the population fairly. Systematic sampling is a symmetrical process where the researcher chooses the samples after a specifically defined interval. Sampling like this leaves the researcher no room for bias regarding choosing the sample.
Let us suppose that N sampling units are
serially numbered from 1 to N some order and a sample of size n is to be drawn
such that N=nk => k=(N/n) where k, usually called the sampling interval , is
an integer.
Systematic
sampling consists in drawing a random number, says i<= k and selecting the
unit corresponding to this number and every kth unit subsequently. Thus the
sample of size n will consist of units I, i+k, i+2k, …., i+(n-1)k. The random
number ‘I’ is called the random start and its value determines, as a matter of
the fact, the whole sample.
Types of Systematic Sampling : Here are the types of systematic sampling:
(a) Systematic random sampling (b) Linear systematic sampling (c) Circular systematic sampling.
Important Formulas and few important Results
Estimation of population mean : When N = nk:
- The sample
mean provides an unbiased estimate of the population mean.
- The
variance of the estimate is
- Comparison with SRSWOR:
![]()
Estimation of population mean : When N not equal to nk:
· The sample mean provides an unbiased estimate of the population mean.
![]()
- The
variance is given as
·
![]()
- In
systematic sampling with sampling interval k from a population with size
N not equal to nk, an unbiased estimator of the population mean Y
is given by
where i stands for the ith systematic
sample, i =1,2,...,
k and n' denotes the size of ith systematic
sample.
When to use systematic sampling
Some
practical situations where systematic sampling has been found very useful are
given as follows:
· The
selection of every kth strip in the forest survey for estimation of timber.
Because of its operational convenience, the job of collecting the systematic sample can be entrusted to the field worker.
Here are 4
other situations of when to use Systematic Sampling:
1. Budget
restrictions: In
comparison to other sampling methods like simple random sampling, this sampling
technique is more suitable for conditions where there are budget restrictions
and also the extremely uncomplicated accomplishment of the study.
Advantage of Systematic Sampling
Here are the advantages of systematic sampling:
· Systematic
sampling is operationally more convenient than simple random sampling or
stratified random sampling. Time and work involved is also relatively much
less.
· Systematic Sampling yields a sample which is evenly spread over the entire population.
· It’s extremely simple and convenient for the researchers to create, conduct, analyze samples.
· As
there’s no need to number each member of a sample, it is better for
representing a population in a faster and simpler manner.
Limitations of Systematic Sampling
Systematic sampling has a number of disadvantages as mentioned below:
·The main disadvantage of systematic sampling is that systematic samples are not in general random samples since the requirement in merit two is rarely fulfilled.
· If N is not a multiple of n, then
(ii) sample mean is not an
unbiased estimate of the population mean.
· It is not possible to obtain unbiased estimate of the variance of systematic sampling on the basis of a single sample because a systematic sample is regarded as a sample of one unit(cluster).
· Systematic sampling may yield highly biased estimates if
there are periodic features associated with the sampling interval i.e, if the
frame has a periodic feature and k is equal to or a multiple of the period.
EXPLAINATION OF SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING USING R
We have
considered a dataset which represent the report of the number of forest fires
in India divided by states. The series comprises the period of 3 years (2008 to
2011). The data were obtained from the official website of the India
government. Suppose we want select a random sample of Year 2010-2011 after
every 5th draw.
PROCEDURE







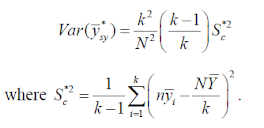







Comments
Post a Comment